Dey Samrat
Hi! I'm Samrat Kumar Dey, currently pursuing my PhD in Informatics with a specialization in Medical Informatics at the University of Missouri-Columbia. Alongside my doctoral studies, I work as a Graduate Research Assistant at the MU Institute for Data Science and Informatics in the Interdisciplinary Data Analytics and Search (iDAS) Lab under the guidance of Prof. Dr. Chi-Ren Shyu. I strongly resonate with the words of the famous American baseball player Babe Ruth, who said, "It’s hard to beat a person who never gives up."
Resaerch Interests
- Machine Learning for Healthcare
- Data analytics & Visualizations
- Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Healthcare Informatics
- Agentic AI
Work Experience
Graduate Research Assistant
University of Missouri-Columbia
Assistant Professor on Study Leave (Computer Science)
Bangladesh Open University (BOU)
Android Application Developer Trainer
National Mobile Application Trainer and Innovation Application Development Program-2015
Education
University of Missouri-Columbia
Military Institute of Science and Technology (MIST),BUP
Patuakhali Science and Technology University (PSTU)
Research Highlights
Analyzing infant cry to detect birth asphyxia using a hybrid CNN and feature extraction approach
Asphyxia, a critical respiratory condition, poses significant risks to newborns and can lead to catastrophic outcomes. Early detection of asphyxia is crucial for reducing infant mortality rates. This study explores feature extraction using Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs), where the features are categorized into time and frequency domains. Data preprocessing techniques, such as noise removal, handling missing values, outliers, and label encoding, are applied to ensure clean data. To address class imbalance, the Random Oversampling (ROS) technique is employed. Hyperparameter optimization is performed using GridSearchCV for various machine-learning models. Deep learning models, including custom artificial neural networks (ANN1) and convolutional neural networks (CNN1, CNN2), are introduced with hidden layers for improved performance. The performance of different ML and DL models is evaluated, with Logistic Regression (LR) achieving an accuracy of 99.16% and a 0.008% error rate. In comparison, ANN1 outperforms other DL models with an accuracy of 98.20% and a 0.018% error rate. The results demonstrate that both ML and DL techniques can significantly enhance early asphyxia detection in newborns. The Logistic Regression model offers the highest accuracy in machine learning, while ANN1 performs optimally in deep learning, suggesting their potential for deployment in clinical settings to improve neonatal care.
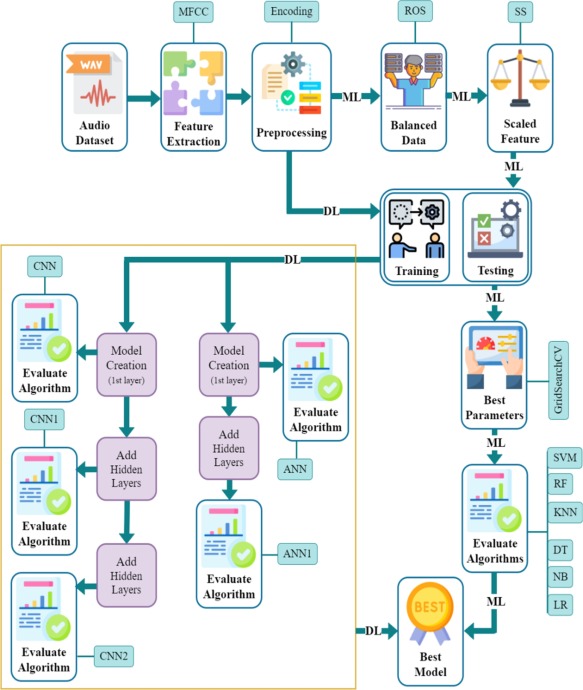
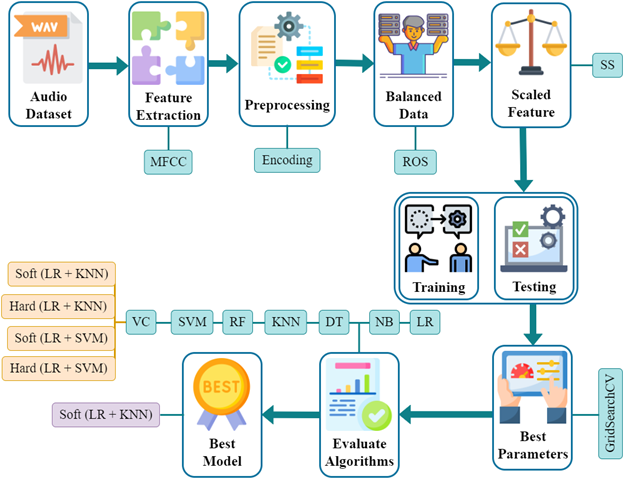
Toward Early Detection of Neonatal Birth Asphyxia Utilizing Ensemble Machine Learning Approach
Perinatal asphyxia is one of the top three causes of neonatal death in developing countries, killing over 1.2 million newborns yearly. Asphyxia cannot be definitively diagnosed early on visually or physically; instead, it can only be diagnosed medically. In this research, an ensemble machine learning-based approach is proposed to detect infant asphyxia at the early stage. Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs), which divide each feature’s values into the time domain and the frequency domain, were originally used in the technique to evaluate feature extraction methodologies. Unwanted noise, outliers, missing numbers, label encoding, and other difficulties are eliminated using pre-processing techniques. By applying the random oversampling (ROS) method, data balance is achieved. After analyzing and evaluating the performance of the proposed model, it is observed that the highest accuracy 99.29% is obtained using the combination of logistic regression and K-nearest neighbor with a 0.007% rate of error.
Prediction of dengue incidents using hospitalized patients, metrological and socio-economic data in Bangladesh: A machine learning approach
Dengue fever is a severe disease spread by Aedes mosquito-borne dengue viruses (DENVs) in tropical areas such as Bangladesh. Since its breakout in the 1960s, dengue fever has been endemic in Bangladesh, with the highest concentration of infections in the capital, Dhaka. This study aims to develop a machine learning model that can use relevant information about the factors that cause Dengue outbreaks within a geographic region. To predict dengue cases in 11 different districts of Bangladesh, we created a DengueBD dataset and employed two machine learning algorithms, Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) and Support Vector Regression (SVR). This research also explores the correlation among environmental factors like temperature, rainfall, and humidity with the rise and decline trend of Dengue cases in different cities of Bangladesh. The entire dataset was divided into an 80:20 ratio, with 80 percent used for training and 20% used for testing. The research findings imply that, for both the MLR with 67% accuracy along with Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 4.57 and SVR models with 75% accuracy along with Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 4.95, the number of dengue cases reduces throughout the winter season in the country and increases mainly during the rainy season in the next ten months, from August 2021 to May 2022. Importantly, Dhaka, Bangladesh’s capital, will see the maximum number of dengue patients during this period. Overall, the results of this data-driven analysis show that machine learning algorithms have enormous potential for predicting dengue epidemics.
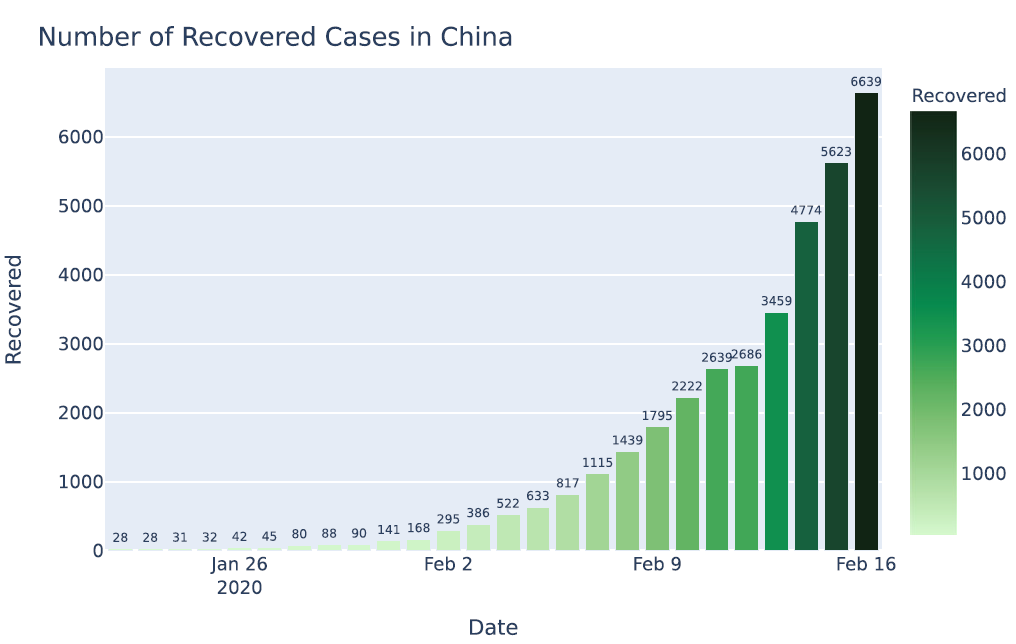
Analyzing the epidemiological outbreak of COVID-19: A visual exploratory data analysis approach
There is an obvious concern globally regarding the fact about the emerging coronavirus 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) as a worldwide public health threat. As the outbreak of COVID-19 causes by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) progresses within China and beyond, rapidly available epidemiological data are needed to guide strategies for situational awareness and intervention. The recent outbreak of pneumonia in Wuhan, China, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 emphasizes the importance of analyzing the epidemiological data of this novel virus and predicting their risks of infecting people all around the globe. In this study, we present an effort to compile and analyze epidemiological outbreak information on COVID-19 based on the several open datasets on 2019-nCoV provided by the Johns Hopkins University, World Health Organization, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, National Health Commission, and DXY. An exploratory data analysis with visualizations has been made to understand the number of different cases reported (confirmed, death, and recovered) in different provinces of China and outside of China. Overall, at the outset of an outbreak like this, it is highly important to readily provide information to begin the evaluation necessary to understand the risks and begin containment activities.
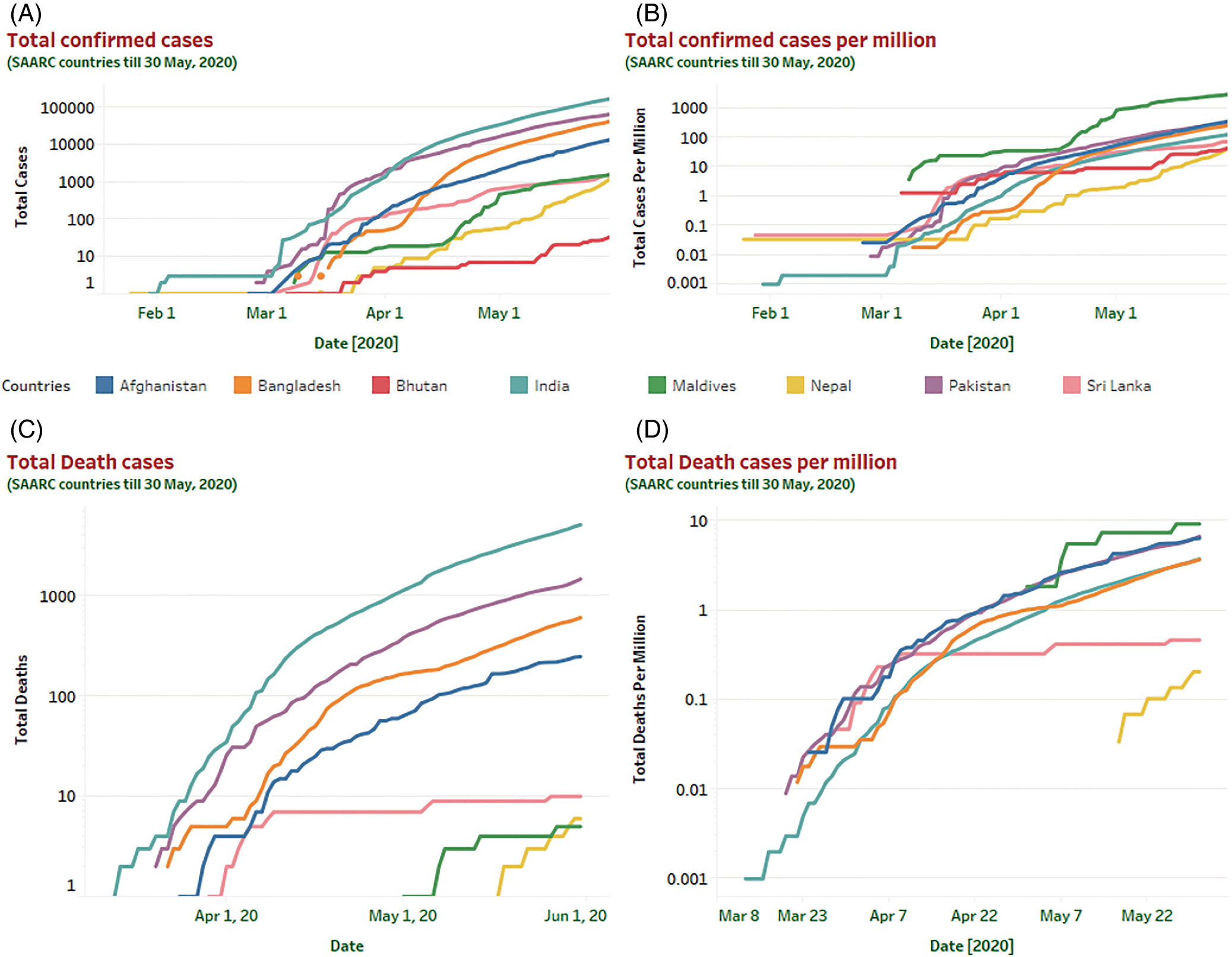
Epidemic trend analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation countries using modified susceptible-infected-recovered predictive model
A novel coronavirus causing the severe and fatal respiratory syndrome was identified in China, is now producing outbreaks in more than 200 countries around the world, and became pandemic by the time. In this article, a modified version of the well-known mathematical epidemic model susceptible-infected-recovered (SIR) is used to analyze the epidemic's course of COVID-19 in eight different countries of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC). To achieve this goal, the parameters of the SIR model are identified by using publicly available data for the corresponding countries: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, the Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka. Based on the prediction model, we estimated the epidemic trend of COVID-19 outbreak in SAARC countries for 20, 90, and 180 days, respectively. A short-mid-long term prediction model has been designed to understand the early dynamics of the COVID-19 epidemic in the southeast Asian region. The maximum and minimum basic reproduction numbers (R0 = 1.33 and 1.07) for SAARC countries are predicted to be in Pakistan and Bhutan. We equate simulation results with real data in the SAARC countries on the COVID-19 outbreak, and predicted different scenarios using the modified SIR prediction model. Our results should provide policymakers with a method for evaluating the impacts of possible interventions, including lockdown and social distancing, as well as testing and contact tracking.
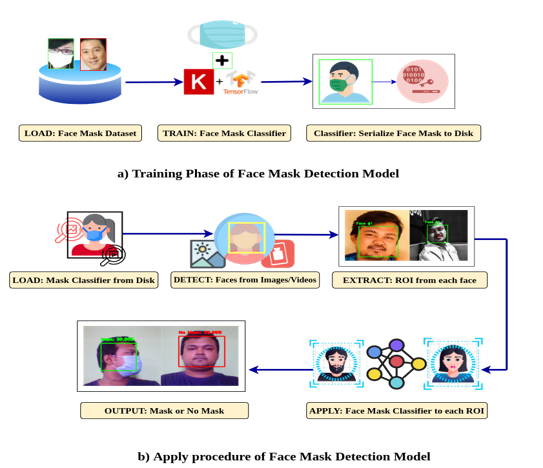
MobileNet Mask: A Multi-phase Face Mask Detection Model to Prevent Person-To-Person Transmission of SARS-CoV-2
Medical researchers around the globe provide evidence that COVID-19 pandemic diseases transmitted through droplets and respirators of respiratory aerosols and wearing a face mask is an efficient infection control recommendation process. In addition, many public and private service providers demand that consumers use the service only if they wear masks properly. However, a few research studies have been found on face mask detection based on the technology of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Image Processing. In this article, we propose, MobileNet Mask, which is a deep learning-based multi-phase face mask detection model for preventing human transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Two different face mask datasets along with more than 5,200 images have been utilized to train and test the model for detecting with and without a face mask from the images and video stream. Experiment results show that with 770 validation samples MobileNet Mask achieves an accuracy of ~ 93% whereas with 276 validation samples it attains an accuracy of nearly ~ 100%. Lastly, we also discuss the possibility of implementing our proposed MobileNet Mask model on light-weighted computing devices such as mobile or embedded devices. Besides, this proposed model also introduces frontier technologies to support the efforts of government and public health guidelines with anticipation of implementing mandatory face mask regulations all over the world.
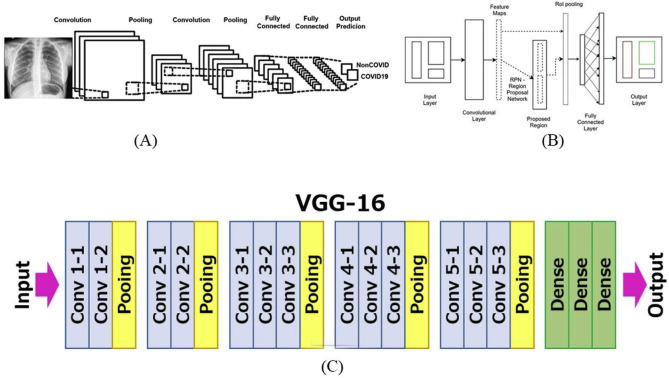
COVID faster R–CNN: A novel framework to Diagnose Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in X-Ray images
COVID-19 or novel coronavirus disease, which has already been declared as a worldwide pandemic, at first had an outbreak in a large city of China, named Wuhan. More than two hundred countries around the world have already been affected by this severe virus as it spreads by human interaction. Moreover, the symptoms of novel coronavirus are quite similar to the general seasonal flu. Screening of infected patients is considered as a critical step in the fight against COVID-19. As there are no distinctive COVID-19 positive case detection tools available, the need for supporting diagnostic tools has increased. Therefore, it is highly relevant to recognize positive cases as early as possible to avoid further spreading of this epidemic. However, there are several methods to detect COVID-19 positive patients, which are typically performed based on respiratory samples and among them, a critical approach for treatment is radiologic imaging or X-Ray imaging. Recent findings from X-Ray imaging techniques suggest that such images contain relevant information about the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Application of Deep Neural Network (DNN) techniques coupled with radiological imaging can be helpful in the accurate identification of this disease, and can also be supportive in overcoming the issue of a shortage of trained physicians in remote communities. In this article, we have introduced a VGG-16 (Visual Geometry Group, also called OxfordNet) Network-based Faster Regions with Convolutional Neural Networks (Faster R–CNN) framework to detect COVID-19 patients from chest X-Ray images using an available open-source dataset. Our proposed approach provides a classification accuracy of 97.36%, 97.65% of sensitivity, and a precision of 99.28%. Therefore, we believe this proposed method might be of assistance for health professionals to validate their initial assessment towards COVID-19 patients.
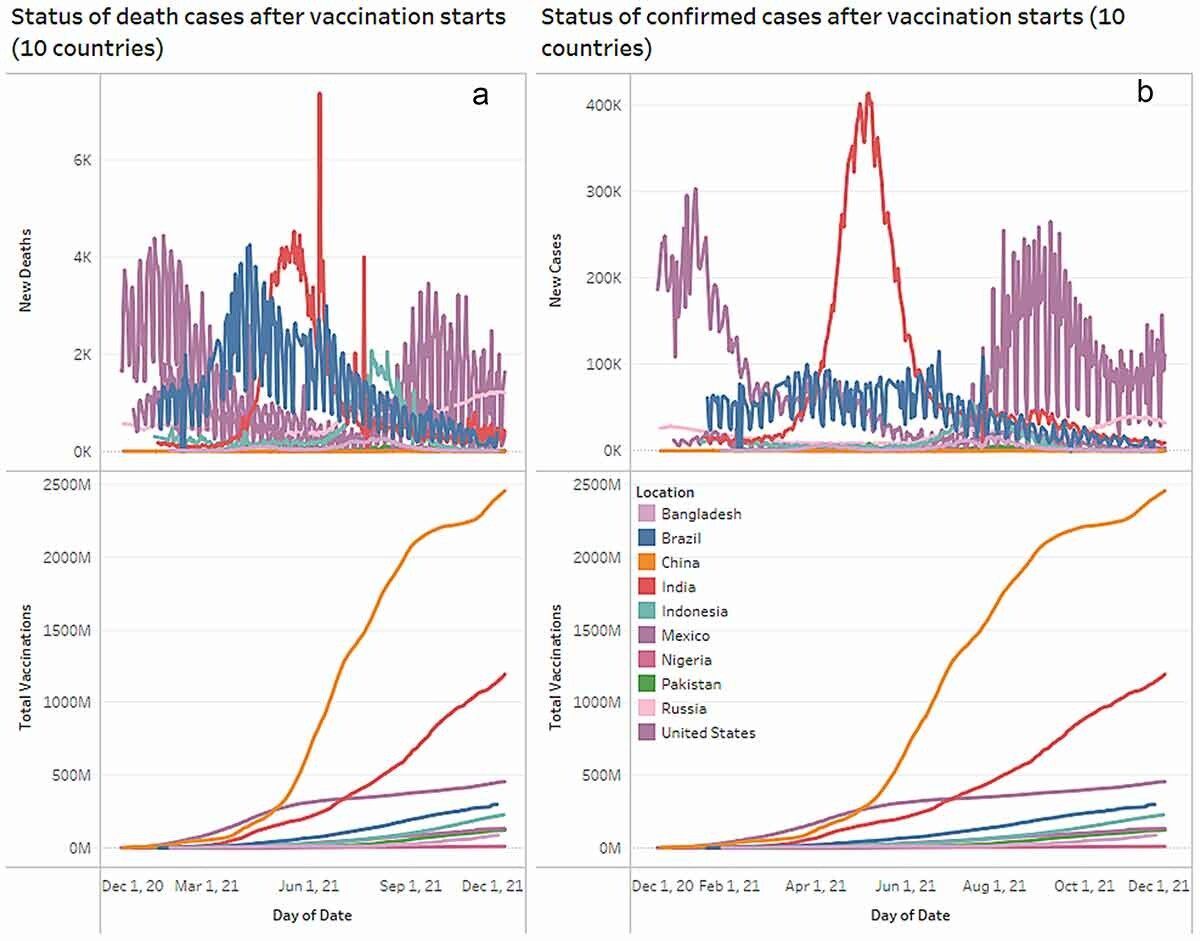
Global landscape of COVID-19 vaccination progress: insight from an exploratory data analysis
The next big step in combating the COVID-19 pandemic will be gaining widespread acceptance of a vaccination campaign for SARS-CoV-2. This study aims to report detailed Spatiotemporal analysis and result-oriented storytelling of the COVID-19 vaccination campaign across the globe. An exploratory data analysis (EDA) with interactive data visualization using various python libraries was conducted. The results show that, globally, with the rapid vaccine development and distribution, people from the different regions are also getting vaccinated and revealing their positive intent toward the COVID-19 vaccination. The outcomes of this exploration also established that mass vaccination campaigns in populated countries including Brazil, China, India, and the US reduced the number of daily COVID-19 deaths and confirmed cases. Overall, our findings contribute to current policy-relevant research by establishing a link between increasing immunization rates and lowering COVID-19’s rising curve.
Feature fusion based VGGFusionNet model to detect COVID-19 patients utilizing computed tomography scan images
COVID-19 or novel coronavirus disease, which has already been declared as a worldwide pandemic, at first had an outbreak in a large city of China, named Wuhan. More than two hundred countries around the world have already been affected by this severe virus as it spreads by human interaction. Moreover, the symptoms of novel coronavirus are quite similar to the general seasonal flu. Screening of infected patients is considered as a critical step in the fight against COVID-19. As there are no distinctive COVID-19 positive case detection tools available, the need for supporting diagnostic tools has increased. Therefore, it is highly relevant to recognize positive cases as early as possible to avoid further spreading of this epidemic. However, there are several methods to detect COVID-19 positive patients, which are typically performed based on respiratory samples and among them, a critical approach for treatment is radiologic imaging or X-Ray imaging. Recent findings from X-Ray imaging techniques suggest that such images contain relevant information about the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Application of Deep Neural Network (DNN) techniques coupled with radiological imaging can be helpful in the accurate identification of this disease, and can also be supportive in overcoming the issue of a shortage of trained physicians in remote communities. In this article, we have introduced a VGG-16 (Visual Geometry Group, also called OxfordNet) Network-based Faster Regions with Convolutional Neural Networks (Faster R–CNN) framework to detect COVID-19 patients from chest X-Ray images using an available open-source dataset. Our proposed approach provides a classification accuracy of 97.36%, 97.65% of sensitivity, and a precision of 99.28%. Therefore, we believe this proposed method might be of assistance for health professionals to validate their initial assessment towards COVID-19 patients.
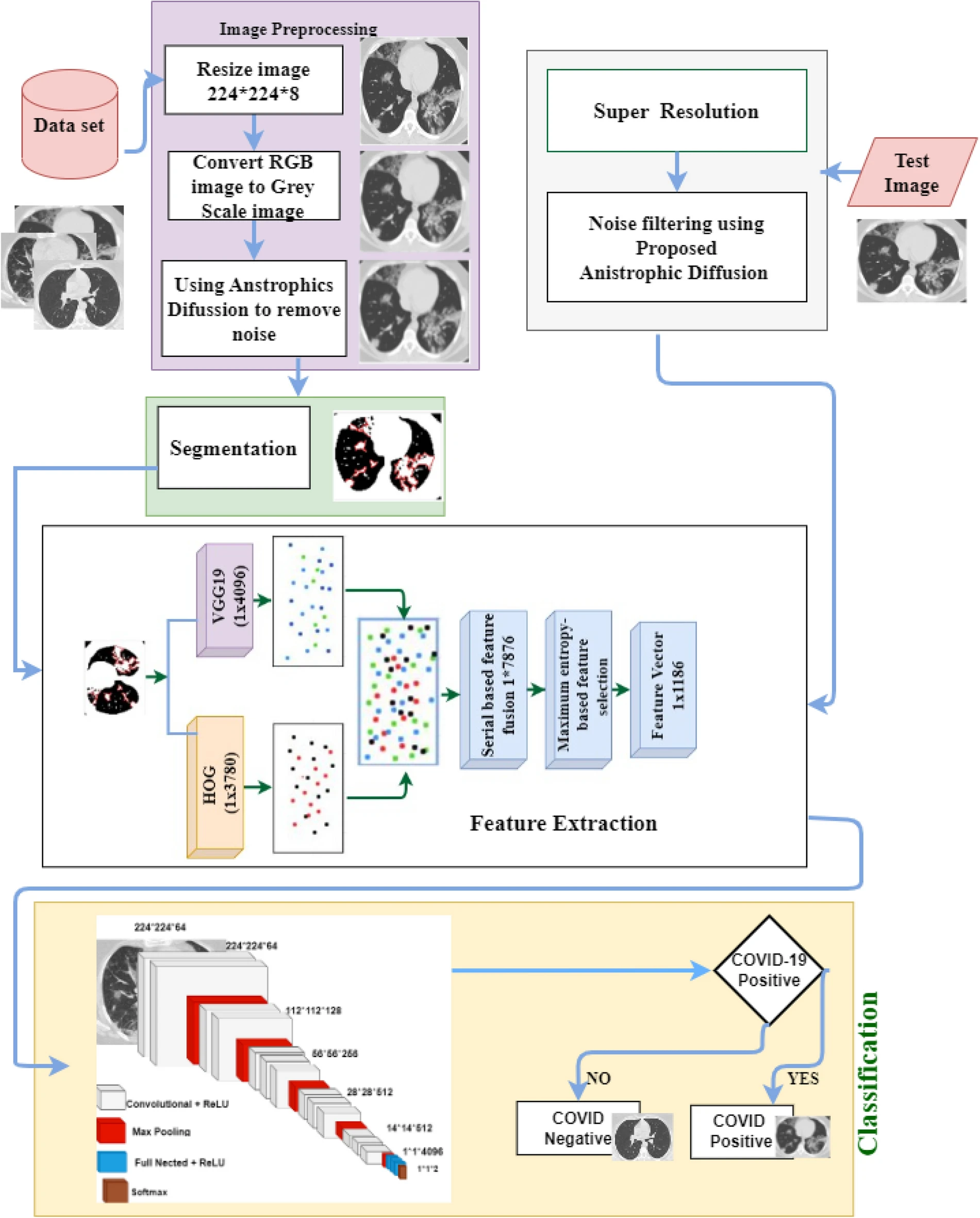
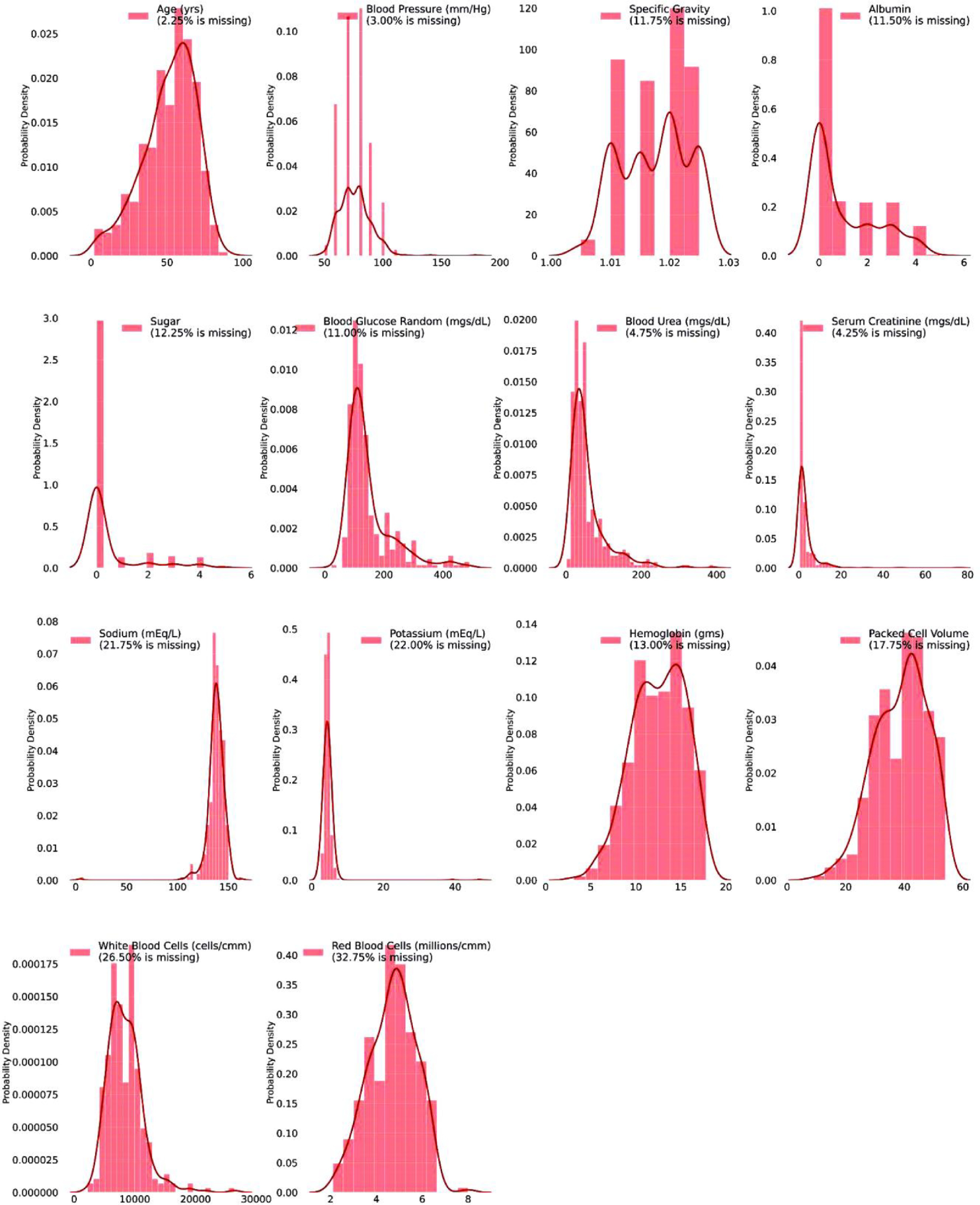
Chi2-MI: A hybrid feature selection based machine learning approach in diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
Early detection and characterization are considered crucial in treating and controlling the chronic renal disease. Because of the rising number of patients, the high risk of progression to end-stage renal disease, and the poor prognosis of morbidity and mortality, chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant burden on the healthcare system. Detecting CKD in its early stages is critical for saving millions of lives. The uniqueness of this study lies in developing a diagnosis system to detect chronic kidney disease using different Machine Learning (ML) algorithms with the support of a hybrid feature selection approach. This study exploited the 400 clinical data of CKD patients based on the dataset supplied by the University of California Irvine (UCI) available at their Machine Learning repository. Different data preparation techniques like encoding categorical features, missing values imputation, removing outlier factors, handling data imbalance, scaling data at the same level, and selecting relevant features are adopted to prepare the dataset for the prediction model. A hybrid Chi-squared test (Chi2) and Mutual Information (MI) based feature selection approach is proposed to remove redundant features, and a Pearson correlation matrix is also computed to consider the top important features for the prediction. Lastly, the Extra tress classifier can diagnose CKD with 98% accuracy and a 2% true negative rate without data leakage out of 14 machine learning models. On the other hand, the Bagging classifier performed worst with only 60% accuracy.
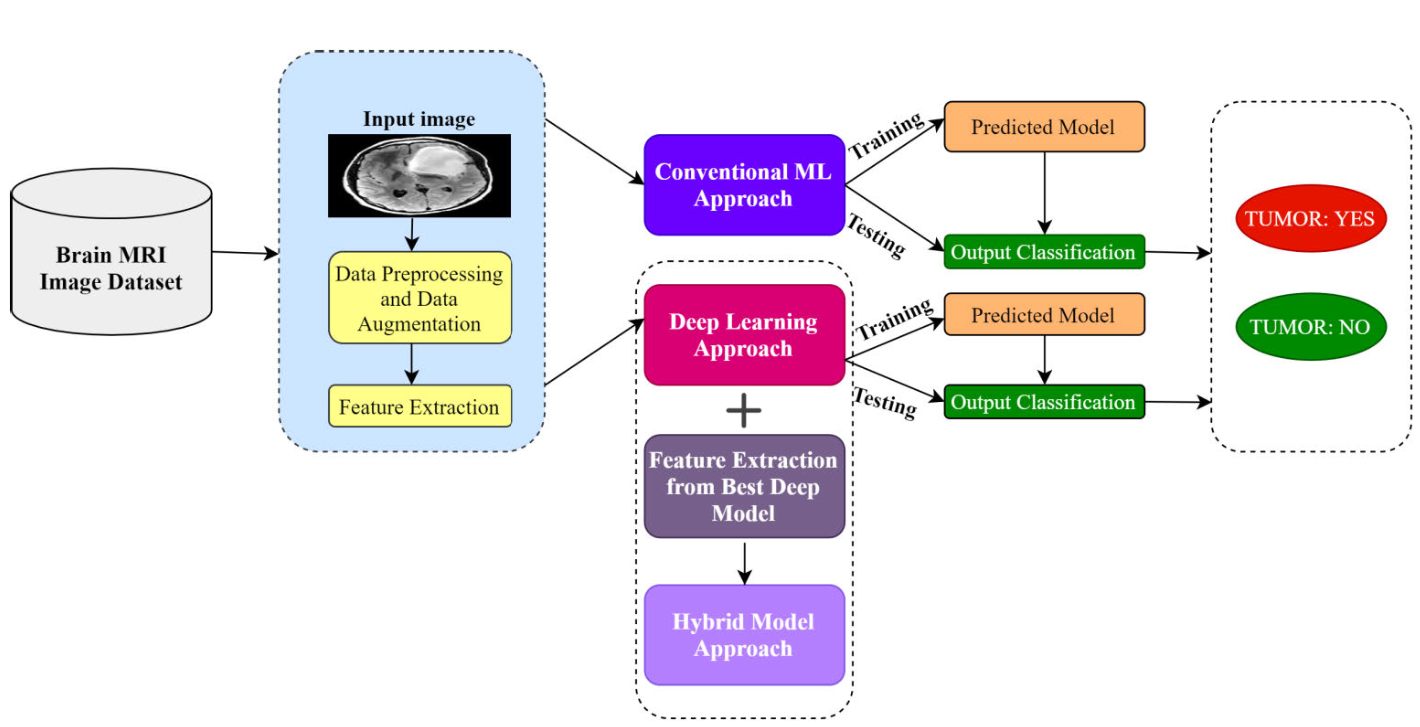
VGG-SCNet: A VGG Net-Based Deep Learning Framework for Brain Tumor Detection on MRI Images
A brain tumor is a life-threatening neurological condition caused by the unregulated development of cells inside the brain or skull. The death rate of people with this condition is steadily increasing. Early diagnosis of malignant tumors is critical for providing treatment to patients, and early discovery improves the patient’s chances of survival. The patient’s survival rate is usually very less if they are not adequately treated. If a brain tumor cannot be identified in an early stage, it can surely lead to death. Therefore, early diagnosis of brain tumors necessitates the use of an automated tool. The segmentation, diagnosis, and isolation of contaminated tumor areas from magnetic resonance (MR) images is a prime concern. However, it is a tedious and time-consuming process that radiologists or clinical specialists must undertake, and their performance is solely dependent on their expertise. To address these limitations, the use of computer-assisted techniques becomes critical. In this paper, different traditional and hybrid ML models were built and analyzed in detail to classify the brain tumor images without any human intervention. Along with these, 16 different transfer learning models were also analyzed to identify the best transfer learning model to classify brain tumors based on neural networks. Finally, using different state-of-the-art technologies, a stacked classifier was proposed which outperforms all the other developed models. The proposed VGG-SCNet’s (VGG Stacked Classifier Network) precision, recall, and f1 scores were found to be 99.2%, 99.1%, and 99.2% respectively.
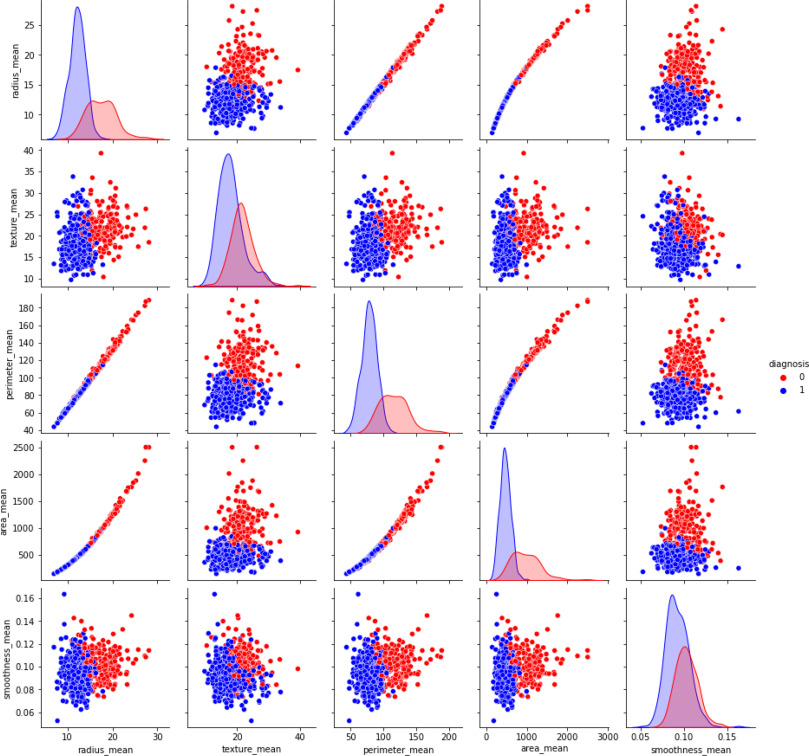
Machine learning-based diagnosis of breast cancer utilizing feature optimization technique
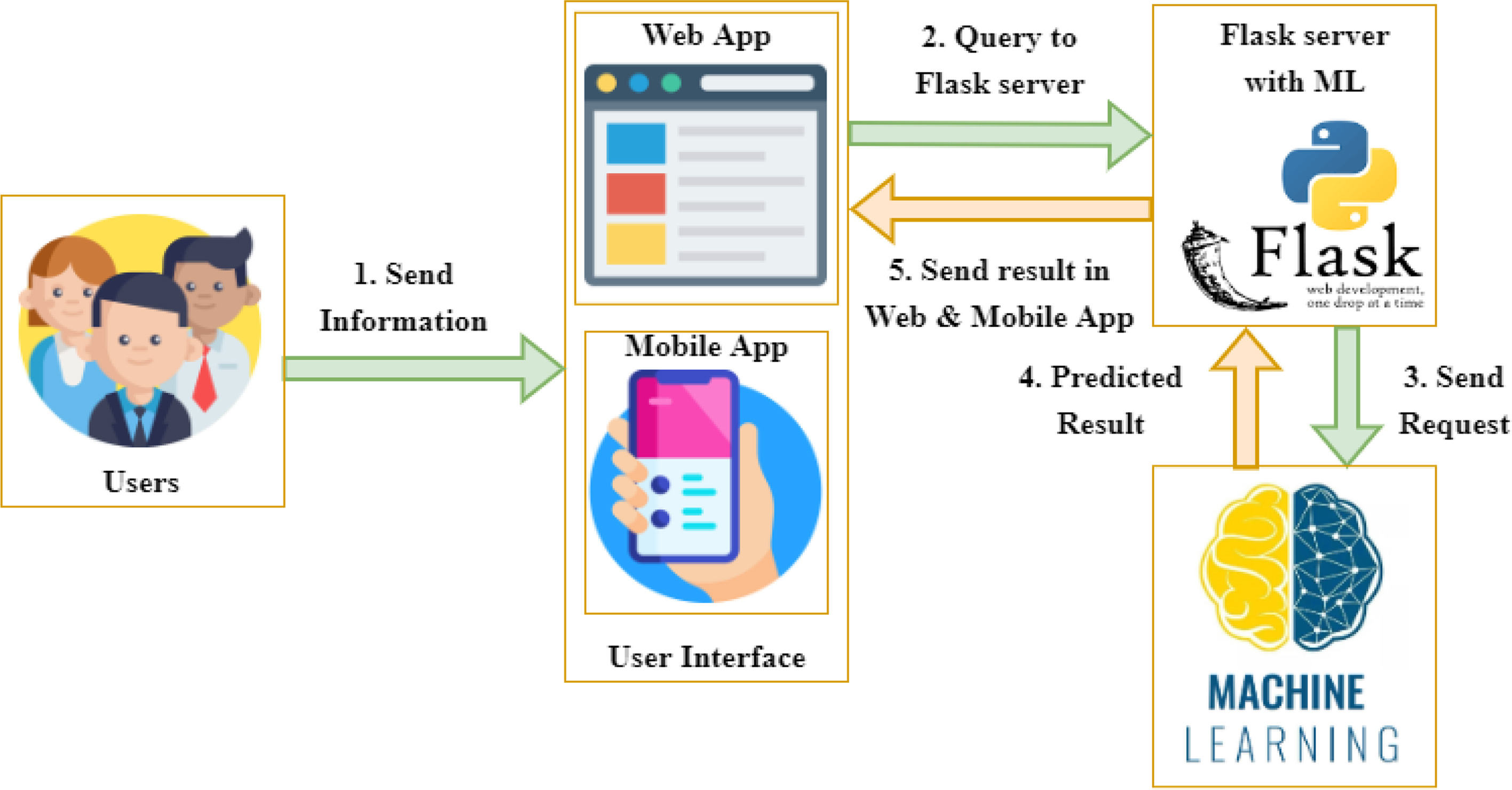
Breast cancer disease is recognized as one of the leading causes of death in women worldwide after lung cancer. Breast cancer refers to a malignant neoplasm that develops from breast cells. Developed and less developed countries both are suffering from this extensive cancer. This cancer can be recuperated if it is detected at an early stage. Many researchers have proposed several machine learning techniques to predict breast cancer with the highest accuracy in the past years. In this research work, the Wisconsin Breast Cancer Dataset (WBCD) has been used as a training set from the UCI machine learning repository to compare the performance of the various machine learning techniques. Different kinds of machine learning classifiers such as support vector machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), K-nearest neighbors(K-NN), Decision tree (DT), Naïve Bayes (NB), Logistic Regression (LR), AdaBoost (AB), Gradient Boosting (GB), Multi-layer perceptron (MLP), Nearest Cluster Classifier (NCC), and voting classifier (VC) have been used for comparing and analyzing breast cancer into benign and malignant tumors. Various matrices such as error rate, Accuracy, Precision, F1-score, and recall have been implemented to measure the model's performance. Each Algorithm's accuracy has been ascertained for finding the best suitable one. Based on the analysis, the result shows that the Voting classifier has the highest accuracy, which is 98.77%, with the lowest error rate. Finally, a web page is developed using a flask micro-framework integrating the best model using react.
A comparative analysis of machine learning classifiers for stroke prediction: A predictive analytics approach
Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the world. It is a dangerous health disorder caused by the interruption of the blood flow to the brain, resulting in severe illness, disability, or death. An accurate prediction of stroke is necessary for the early stage of treatment and overcoming the mortality rate. This study proposes a machine learning approach to diagnose stroke with imbalanced data more accurately. Random Over Sampling (ROS) technique has been used in this work to balance the data. Eleven classifiers, including Support Vector Machine, Random Forest, K-nearest Neighbor, Decision Tree, Naïve Bayes, Voting Classifier, AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting, Multi-Layer Perception, and Nearest Centroid, are analyzed in this study. Ten classifiers show more than 90% accurate results before balancing the data and four classifiers display more than 96% accurate results after data-balancing using the oversampling method. The Hyperparameter tuning and cross-validation are performed in each model to enhance the results. Moreover, Accuracy, F1-Measure, Precision, and Recall are used to measure the performance of machine learning models. The results show the Support Vector Machine has the highest accuracy of 99.99%, with recall values of 99.99%, precision values of 99.99%, and F1-measure of 99.99%. Random Forest achieves the second-highest accuracy of 99.87%, with a 0.001% error. In addition, a user-friendly web app and a user-friendly mobile app are built based on the most accurate model.
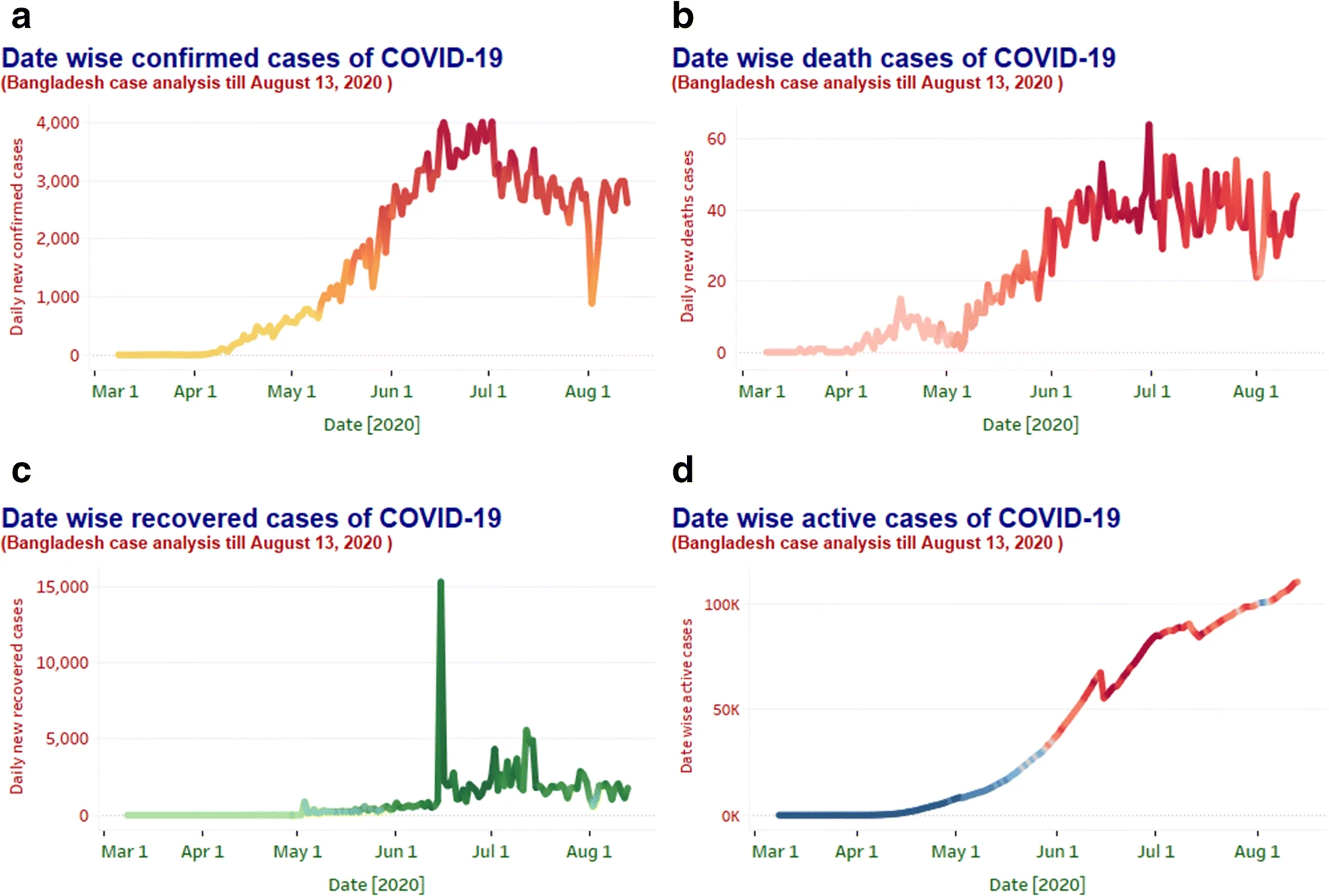
Exploring Epidemiological Behavior of Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19) Outbreak in Bangladesh
Globally, there is an obvious concern about the fact that the evolving 2019-nCoV coronavirus is a worldwide public health threat. The appearance of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in China at the end of 2019 triggered a major global epidemic, which is now a major community health issue. As of August 13, 2020, according to the Institute of Epidemiology, Disease Control and Research (IEDCR), Bangladesh has reported 269,095 confirmed cases between 8 March and 13 August 2020, with > 1.30% of mortality rate and > 57% of recovery rate. COVID-19 outbreak is evolving so rapidly in Bangladesh; therefore, the availability of epidemiological data and its sensible analysis are essential to direct strategies for situational awareness and intervention. This article presents an exploratory data analysis approach to collect and analyze COVID-19 data on epidemiological outbreaks based on the first publicly available COVID-19 Daily Dataset of Bangladesh. Various publicly open data sources on the outbreak of COVID-19 provided by the IEDCR, World Health Organization (WHO), Directorate General of Health Services (DGHS), and Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MHFW) of Bangladesh have been used in this research. Visual exploratory data analysis (V-EDA) techniques have been followed in this research to understand the epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19 outbreak in different districts of Bangladesh between 8 March 2020 and 13 August 2020 and these findings were compared with those of other countries. In all, this is extremely important to promptly spread information to understand the risks of this pandemic and begin containment activities in the country.
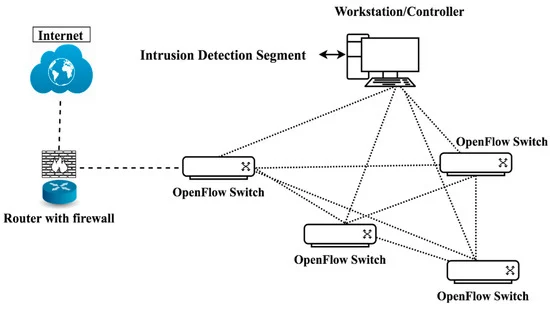
Effects of Machine Learning Approach in Flow-Based Anomaly Detection on Software-Defined Networking
Recent advancements in software-defined networking (SDN) make it possible to overcome the management challenges of traditional networks by logically centralizing the control plane and decoupling it from the forwarding plane. Through a symmetric and centralized controller, SDN can prevent security breaches, but it can also bring in new threats and vulnerabilities. The central controller can be a single point of failure. Hence, flow-based anomaly detection system in OpenFlow Controller can secure SDN to a great extent. In this research, we investigated two different approaches of flow-based intrusion detection system in OpenFlow Controller. The first of which is based on machine-learning algorithm where NSL-KDD dataset with feature selection ensures the accuracy of 82% with random forest classifier using the gain ratio feature selection evaluator. In the later phase, the second approach is combined with a deep neural network (DNN)-based intrusion detection system based on gated recurrent unit-long short-term memory (GRU-LSTM) where we used a suitable ANOVA F-Test and recursive feature elimination selection method to boost classifier output and achieve an accuracy of 88%. Substantial experiments with comparative analysis clearly show that, deep learning would be a better choice for intrusion detection in OpenFlow Controller.
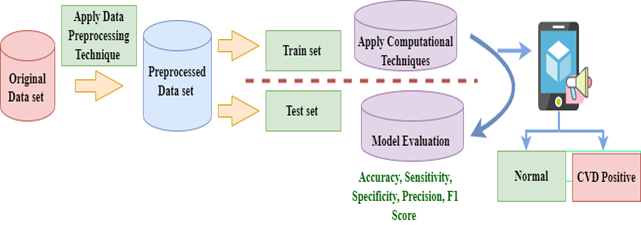
A Voice Assistive Mobile Application Tool to Detect Cardiovascular Disease Using Machine Learning Approach
Many people all around the world suffer from heart disease, which is regarded as a severe illness. In healthcare, especially cardiology, it is crucial to accurately and quickly diagnose cardiac problems. In this research, we proposed an accurate and efficient mobile application-based system for diagnosing cardiac disease based on machine learning approaches. The developed mobile application is voice assistive, which makes the proposed application more user-friendly. Numerous machine learning methods have been examined in this study to predict and diagnose cardiovascular disease (CVD). A detailed comparative study was also drawn using eighteen (18) classification algorithms such as Support Vector Machines, Logistic Regression, Linear SVC, K-Nearest Neighbors, Naive Bayes, Stochastic Gradient Descent, Gradient Boosting, Ridge, Bagging, Random Forest, Decision Tree, XGB, LGBM, Extra Trees Perceptron, and Voting Classifier (hard or soft voting). Sixty-eight thousand nine hundred seventy-five (68,975) samples from various patients were used to test the performance of each approach. According to the study, Random Forest and Decision Trees have the best accuracy levels at 99.9%. However, the Support Vector Machine classifier had the lowest performance, barely achieving 60% accuracy.
Research Publication
Published Journal
[J25]. Dey, S.K., Uddin, K.M.M., Howlader, A., Rahman, M.M., Babu, H.M.H., Biswas, N., and Mazumder, B. (2025). Analyzing Infant Cry to Detect Birth Asphyxia Using a Hybrid CNN and Feature Extraction Approach Neuroscience Informatics. (Available at Elsevier)
[J24]. Setu, D.M., Islam, T., Erfan, Md., Dey, S.K., Asif, Md. R.A., and Samsuddoha, Md. (2025). A comprehensive strategy for identifying plagiarism in academic submissions J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Eng. Archit. (Available at Springer)
[J23]. Sifath, S., Islam, T., Erfan, M., Dey, S. K., Islam, M. M. U., Samsuddoha, M., & Rahman, T. (2024). Recurrent neural network based multiclass cyber bullying classification. Natural Language Processing Journal, 100111. (Available at Elsevier)
[J22]. Qazi, A., Hasan, N., Mao, R., Abo, M. E. M., Dey, S. K., & Hardaker, G. (2024). Machine Learning-Based Opinion Spam Detection: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access. (Available at IEEE Access)
[J21]. TKundu, D., Rahman, M. M.,Dey, S. K., Rahman, A., Das, D., Siddiqi, U. R., Alam, M. G. R., ... & Ali, Z. (2024). Federated deep learning for monkeypox disease detection on gan-augmented dataset. IEEE Access. (Available at IEEE Access)
[J20]. Taifa, I. A., Setu, D. M., Islam, T., Dey, S. K., & Rahman, T. (2024). A hybrid approach with customized machine learning classifiers and multiple feature extractors for enhancing diabetic retinopathy detection. Healthcare Analytics, 100346. (Available at Elsevier)
[J19]. Uddin, K. M. M., Nahid, M. N. H., Ullah, M. M. H., Mazumder, B., Khan, M. S. I., & Dey, S. K. (2024). Machine Learning-Based Chronic Kidney Cancer Prediction Application: A Predictive Analytics Approach. Biomedical Materials & Devices, 2(2), 1028-1048. (Available at Springer)
[J18]. Uddin, K. M. M., Dey, S. K., & Babu, H. M. H. (2024). A Voice assistive mobile application tool to detect cardiovascular disease using machine learning approach. Biomedical Materials & Devices, 2(2), 1246-1257. (Available at Springer)
[J17]. Uddin, K. M. M., Al Mamun, A., Chakrabarti, A., Mostafiz, R., & Dey, S. K. (2024). An ensemble machine learning-based approach to predict cervical cancer using hybrid feature selection. Neuroscience Informatics, 4(3), 100169. (Available at Elsevier)
[J16]. Uddin, K. M. M., Biswas, N., Rikta, S. T., & Dey, S. K. (2023). Machine learning-based diagnosis of breast cancer utilizing feature optimization technique. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine Update, 3, 100098. (Available at Elsevier)
[J15]. Dey, S. K., Rahman, M. M., Shibly, K. H., Siddiqi, U. R., & Howlader, A. (2023). Epidemic trend analysis of SARS‐CoV‐2 in South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation countries using modified susceptible‐infected‐recovered predictive model. Engineering Reports, 5(1), e12550. (Available at Wiley)
[J14]. Uddin, K. M. M., Dey, S. K., Babu, H. M. H., Mostafiz, R., Uddin, S., Shoombuatong, W., & Moni, M. A. (2022). Feature fusion based VGGFusionNet model to detect COVID-19 patients utilizing computed tomography scan images. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 21796. (Available at Spriger Nature)
[J13]. Dey, S. K., Uddin, K. M. M., Babu, H. M. H., Rahman, M. M., Howlader, A., & Uddin, K. A. (2022). Chi2-MI: A hybrid feature selection based machine learning approach in diagnosis of chronic kidney disease. Intelligent Systems with Applications, 16, 200144. (Available at Elsevier)
[J12]. Biswas, N., Uddin, K. M. M., Rikta, S. T., & Dey, S. K. (2022). A comparative analysis of machine learning classifiers for stroke prediction: A predictive analytics approach. Healthcare Analytics, 2, 100116. (Available at Elsevier)
[J11]. Rahman, M. M., Kundu, D., Suha, S. A., Siddiqi, U. R., & Dey, S. K. (2022). Hospital patients’ length of stay prediction: A federated learning approach. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 34(10), 7874-7884. (Available at Elsevier).
[J10]. Dey, S. K., Rahman, M. M., Howlader, A., Siddiqi, U. R., Uddin, K. M. M., Borhan, R., & Rahman, E. U. (2022). Prediction of dengue incidents using hospitalized patients, metrological and socio-economic data in Bangladesh: A machine learning approach. PloS one, 17(7), e0270933. (Available at PLoS ONE)
[J9]. Dey, S. K., Rahman, M. M., Siddiqi, U. R., Howlader, A., Tushar, M. A., & Qazi, A. (2022). Global landscape of COVID-19 vaccination progress: insight from an exploratory data analysis. Human vaccines & immunotherapeutics, 18(1), 2025009. (Available at Taylor and Francis)
[J8]. Alghazzawi, D., Qazi, A., Qazi, J., Naseer, K., Zeeshan, M., Abo, M. E. M.,Dey, S. K., & Yang, S. (2021). Prediction of the infectious outbreak COVID-19 and prevalence of anxiety: global evidence. Sustainability, 13(20), 11339. (Available at MDPI)
Book Chapter
Conferences
GRANTS and PROJECTS
Classification of Infant Cry for Detection of Birth Asphyxia on Baby Chillanto Database Using Deep and Machine Learning Approaches
Predicting Crops Yield for Smallholder Farmers: A Data-Driven Approach with Hybrid (CNN-LSTM) Deep Model
Identifying the role of ChatGPT in Teaching and Learning Practice
Alignment and Evaluation of Course Outcome and Program Outcome in the Context of Students Learning Experience at BOU: OBE-based Web Application Architecture
MUJIB BORSHO IT CARNIVAL 2020
ParkEsay: An Smartphone Based Approach to Mitigate Car Parking Problems Using IoT at Dhaka City
Study the Challenges and Opportunities of Mobile Health in Bangladesh: Regional Exposures and Health Consequences in Context to Bangladesh
Skills
- Tableau
- QGIS
- Ploly, ggplot, Keras, Google Colab
- Scikit-learn & Matplotlib
Teaching Experiences
Theory Courses
- CSE2135: Data Structure
- CSE2137: Object Oriented Programming
- CSE2234: Information System Analysis and Design
- CSE3232: Human-Computer Interaction
- CSE4133: Artificial Intelligence
- CSE4234: Mobile Application Development
Lab Courses
- CSE21P6: Data Structure Lab
- CSE21P8: Object Oriented Programming-I Lab
- CSE22P5: Information System Analysis and Design Lab
- CSE31P8: Object Oriented Programming-II Lab
- CSE41P4: Artificial Intelligence Lab
- CSE42P5: Mobile Application Development Lab
Awards & Honours
- Nominated to India Science and Research Fellowship 2024-25, Bangladesh Academy of Science (BAS)
- AI for Good-Innovate for Impact Award, AI for Good Global Summit, ITU, WAIC 2024
- Most Accurate Deep Model Creator, AI in Public Health Workshop 2024
- Group Lead, Innovation Fair Award 2024, BOU Innovation Unit
- Judge, Bangladesh Robot Olympiad 2024, 2023, 2022, 2021
- Regional Judge & Mentor, NASA Space Apps Challenge 2023, 2022, 2021, 2020
- Judge, BASIS National ICT Award 2022
- Final Round Judge, BDApss National Hackathon 2022
- Convener, Mujib Borsho IT Carnival 2020
- Best Project Supervisor Award, Department of CSE, Dhaka International University
- Best Mobile App Developer Award, National Mobile Application Awareness Development and Training Program 2015
Networks
- Lead Guest Editor, Special Issue on Data-Driven Decision Making in Healthcare Informatics
- Academic Editor, PLoS ONE, Public Library of Science
- Academic Editor, Journal of Computational and Mathematical Methods, Wiley
- Professional Member, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
- Professional Member, Association for Computing Machinery (ACM)
- Member, ACM Special Imterest Group Computer Human Interaction (SIGCHI)
- Advisor, Computer Programming Club (CPC), Bangladesh Open University
- Member Affairs Secretary, Bangladesh Data Science Society (BDDSS)
- Former Faculty Advisor, CodeChef Chapter, Dhaka International University
- Former Mentor,BASIS Students Forum, Dhaka International University
- Associate Member, Bangladesh Computer Society
- Former Advisor, Computer Programming Club (CPC), Dhaka International University